Virtualization Providers
This section describes how to manage hypervisors and their managers in vPlus. Inventory that vPlus needs first to be populated. The first step is always to add a hypervisor manager (if its virtualization platform supports a dedicated manager) or individual hypervisors (if these are not managed, but are stand-alone).
You also can verify if your Hypervisor Storage (datastores/storage repositories/storage domains, depending on how different platforms call it) or Hypervisor Clusters (which corresponds to server pools/ clusters/availability zones) have been detected.
When adding a new Virtulization provider, you always need to provide:
URL (hypervisor manager - valid URLs are described in the sections describing the setup of a particular virtual platform type) or hostname/IP (hypervisor)
the node which is responsible for executing tasks in this environment
backup strategy - if available for a particular platform
Then synchronize inventory (either automatically - there will be a dialog box shown just after saving the form, or manually with the button on the right of the hypervisor or manager). If Inventory Synchronization tasks (visible in the console at the bottom) completed successfully, also proves that the connection was successful, credentials are correct and all the inventory items have been collected successfully.
Check Hypervisor Storage, Hypervisor Clusters tabs, as well as Virtual Environments -> Instances to see the results of inventory synchronization
Note.
inventory synchronization executed on the manager level assigns the same node as used for the manager to all hypervisors - you can override it in the Hypervisor tab and assign a different node to handle VMs that reside on a specific hypervisor - this is especially important for scalability and when environments are divided into multiple clusters (disk-attachments strategies may not be able to access disks from different clusters)
if you use disk-attachment strategy - always execute inventory synchronization at least once from each hypervisor - the end result will be the same from the inventory point of view, but each node needs to detect its own Proxy VM ID in the environment to attach disks to the correct VM
The Last successful sync column shows when the inventory synchronization process has been completed successfully - this column should help you to determine if for any reason inventory in vPlus is not out of sync with your infrastructure
Hypervisor clusters and storages
When using Openstack, for each hypervisor cluster and hypervisor storage, you can select projects for which it is going to be available in horizon plugin restore dialog.
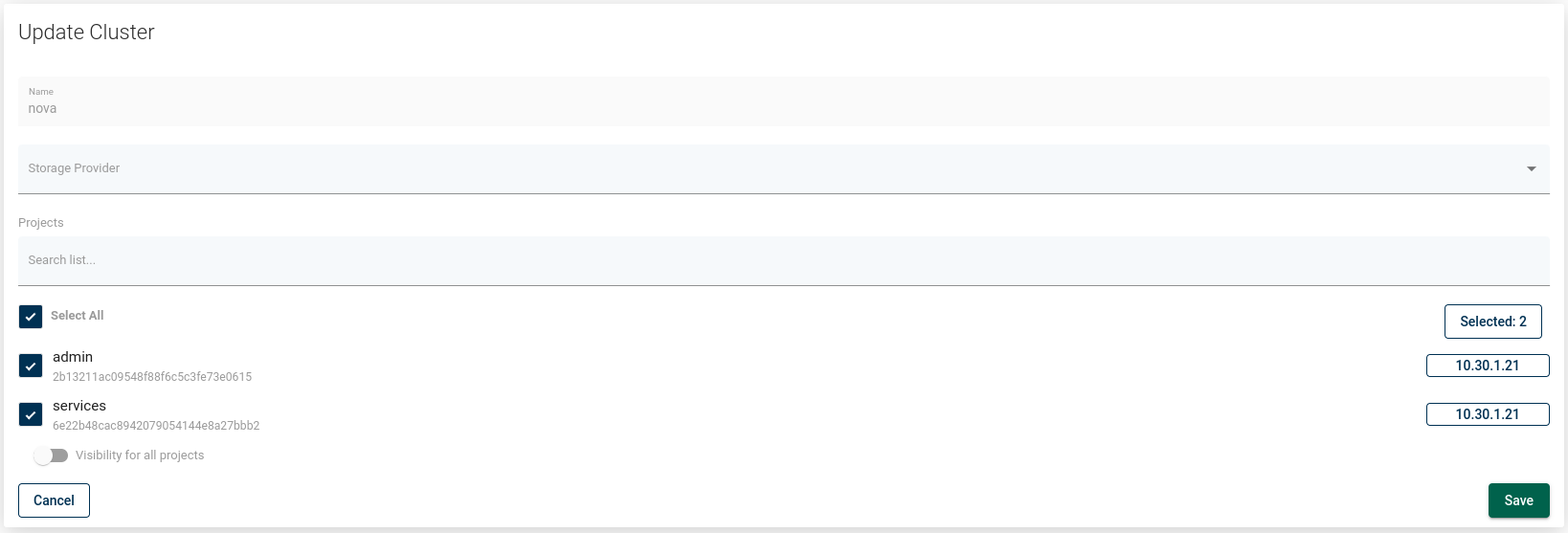
Selecting "Visible for all projects" will make a cluster/storage visible for all projects, regardless of their time of creation (including ones added after editing this setting).
Deselecting "Visible for all projects" option and selecting some (or all) of existing projects will result in cluster/storage being visible just for selected, already existing projects. The cluster/storage will not be automatically visible for any newly added projects.
This setting will also affect filtering clusters and storages by project selected in restore modal dialog or while editing restore setting for recovery plan rule.
Hypervisor SSL certificates management
Note. SSL certificate management is available only for:
Red Hat Virtualization
Citrix Hypervisor (XenServer)
VMware vSphere
When you first time connect to the hypervisor host, the certificate will be fetched and stored. The certificate is used to validate the authenticity of the hypervisor host during the inventory, backup, and restore operations.
If the certificate changes the connection to the hypervisor will be failed, and in the console and logs, you will find proper information.
When you will have a new trusted certificate deployed on the hypervisor host, you can remove an old one from the product, and during the next connection, the new certificate will be fetched and used.
Validating the certificate
To validate fetched certificate:
Go to Virtual Environments -> Virtualization Providers
Click on Hypervisor which certificate you would like to validate
Click Certificates tab
In this view, you can check the certificate fetched from the selected hypervisor host.
Automatically trust all certificates
You can skip the certificate validation and automatically trust all certificates.
Go to Virtual Environments -> Virtualization Providers
Click on Hypervisor which certificate you would like to validate
Click Certificates tab
Turn on switch "Trust all certificates"
Confirm your action
From this moment, the certificates will be not validated.
Removing certificate
To remove stored certificate:
Go to Virtual Environments -> Virtualization Providers
Click on Hypervisor which certificate you would like to validate
Click Certificates tab
Click on Clear button
Confirm your action
The certificate will be removed, and a new certificate will be fetched during the next connection to the hypervisor host.
Quotas
Quotas manage the number of VM backups and restores in projects. Quotas uses user-defined rules to control the number of backups. Each Rule has two thresholds: SOFT and HARD. SOFT limits only warn you when a certain limit is exceeded. HARD limits prevent the execution of tasks that have exceeded the specified limits. When any of the rules are exceeded, the task fails or warnings are placed on the VM and on backup or restore. For each limit type, you need to specify the time frame in which the rule will be applied. Quotas can be activated or deactivated at any moment, additionally each rule can be activated or deactivated.
To create a new Quota, open Infrastructure tab under Virtual Environments section and go to Quotas, then click on Create button on the right.