Instances
General
A list of currently known virtual machines and access to the details page of each object. From this place, you can also perform on-demand actions such as backup, restore, and file-level restore.
The field lets the user filter the virtual machines by their:
Name
UUID
GUID
Tags
URL of a linked hypervisor manager
Node configuration name linked via hypervisor manager
Host field of a linked hypervisor
Node configuration name linked via a hypervisor
Name field of a linked VM Backup Policy
Name field of a linked Snapshot Management Policy
Returning to the VM details page, this is what it looks like:
As you can see, the window has been divided into several areas:
VM Summary

At the top, you can see summarized pieces of information about the VM, such as:
the ID of the VM object into vPlus
to which hypervisor the VM belongs
which node is backing up this virtual machine
short information about the last backup actions
whether the virtual machine has tags or policies assigned to it
You can also use several function buttons:
refresh
back to list
backup
restore
mount
delete
Backup/Restore Statistics
Daily activity
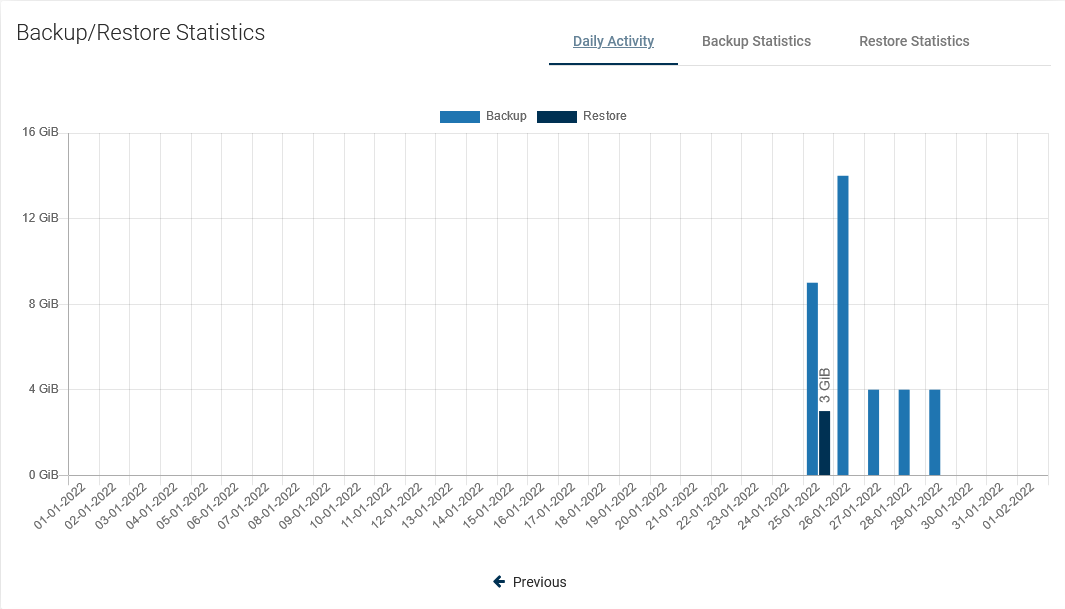
First, you'll see a daily summary of the backup and restore operations for the last month. This view is called "Daily Summary" and is the default view. You can switch the report between four views.
Backup Size
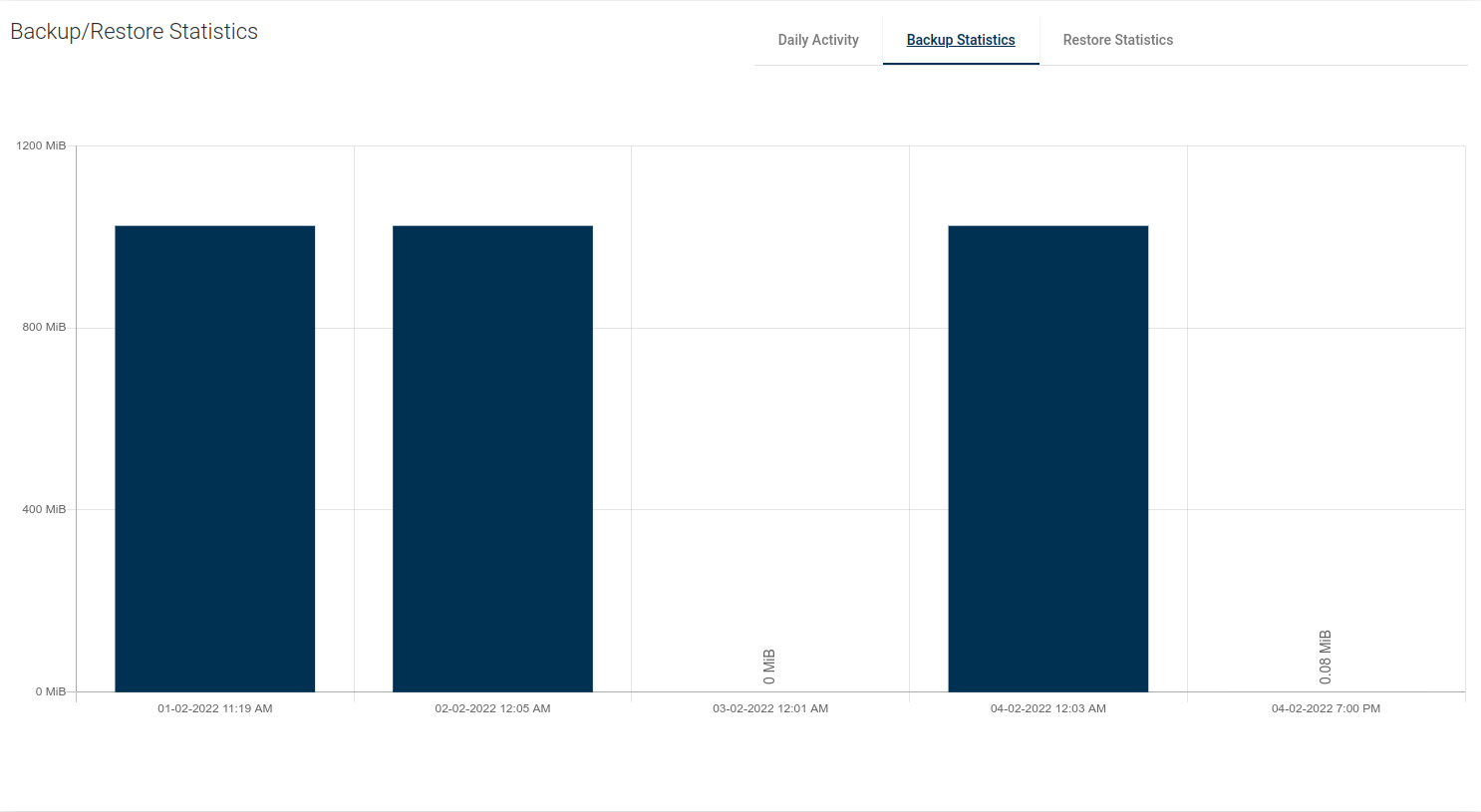
This view shows separate columns for the size of the current backed up data.
Backup Time
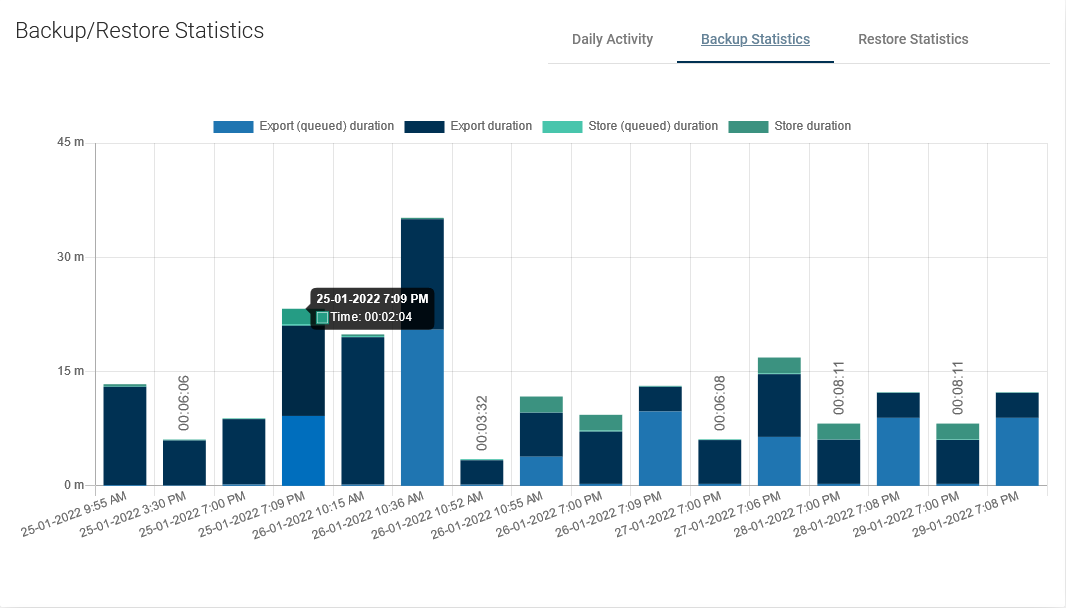
A very useful report. It allows you to determine the required window length for backups or, based on the time of individual phases, it is easy to deduce the cause of slow backups.
Transfer Rate (Backup)
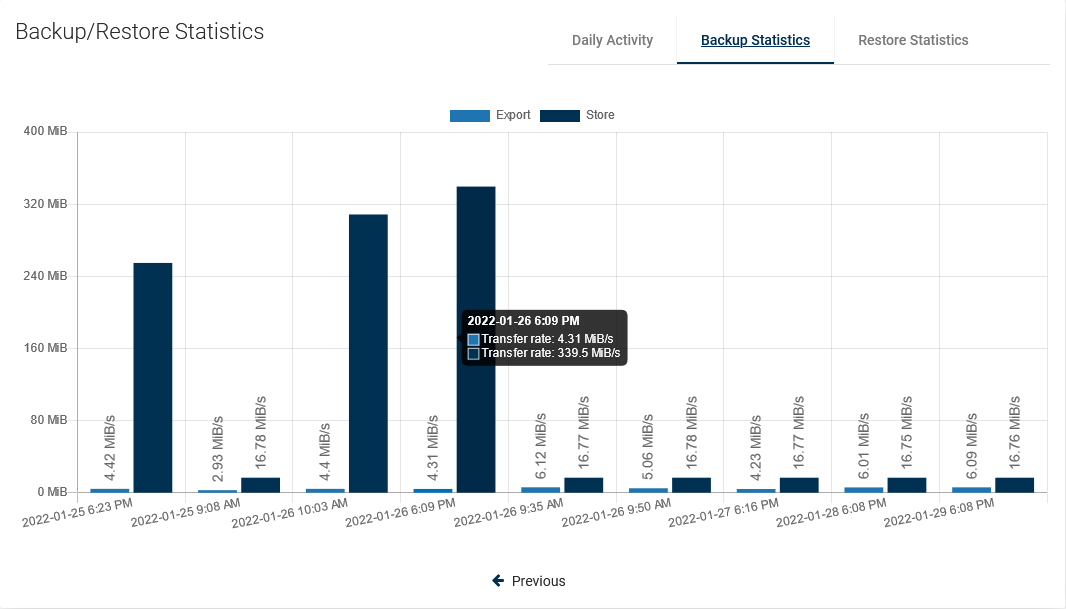
One of the latest reports, now you can easily see how fast data transfer is.
Restore Time
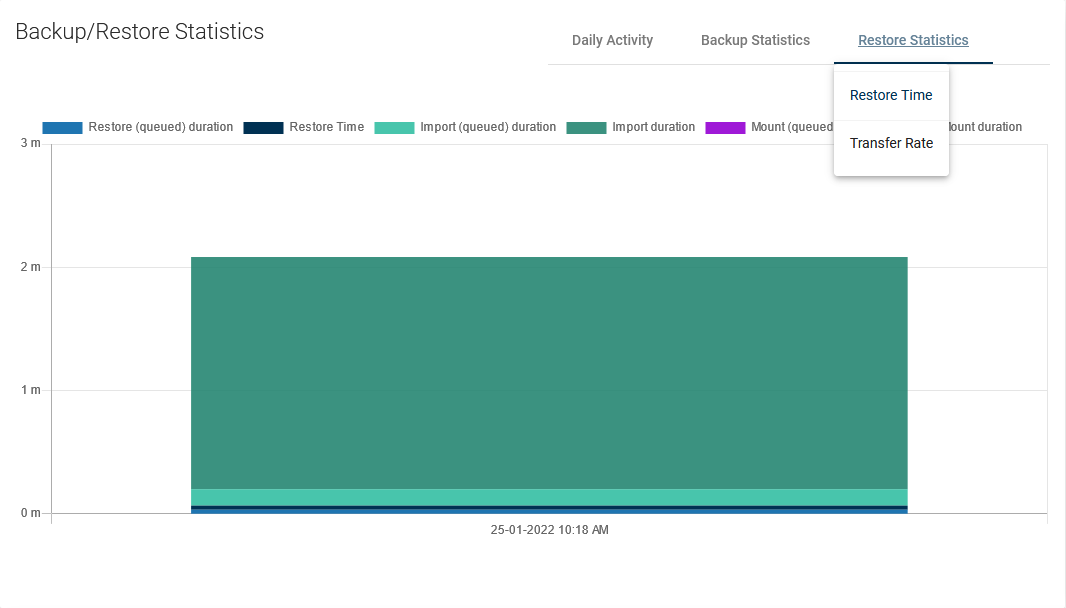
A view with the same properties as "Backup Time". It allows us to estimate how long it will take to restore the machine in the event of a failure.
Transfer Rate (Restore)
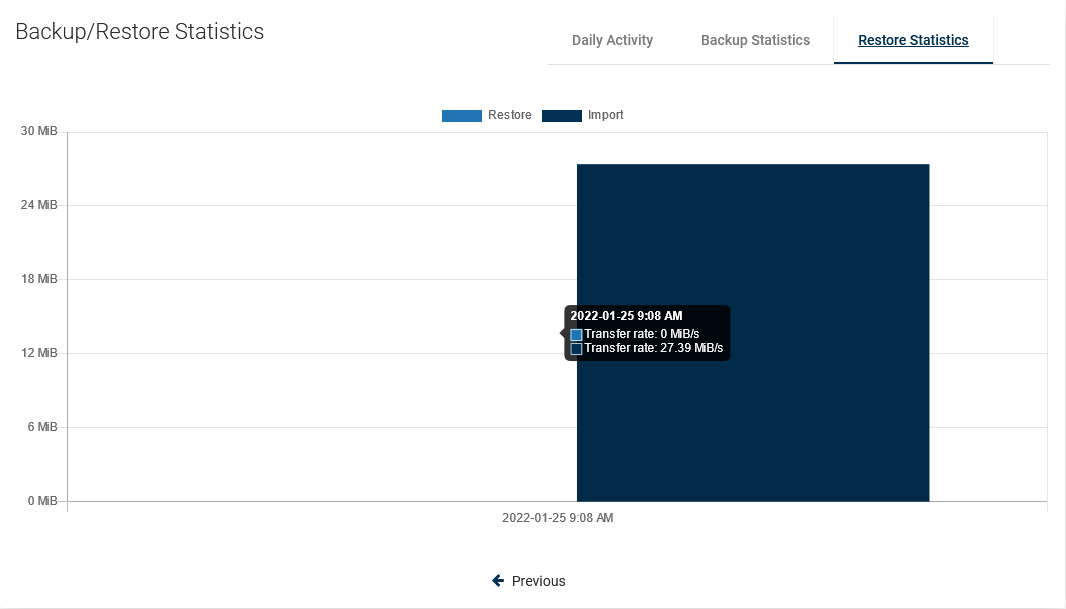
As in the previous case, we also have the transfer speed for the restore job.
Events Calendar
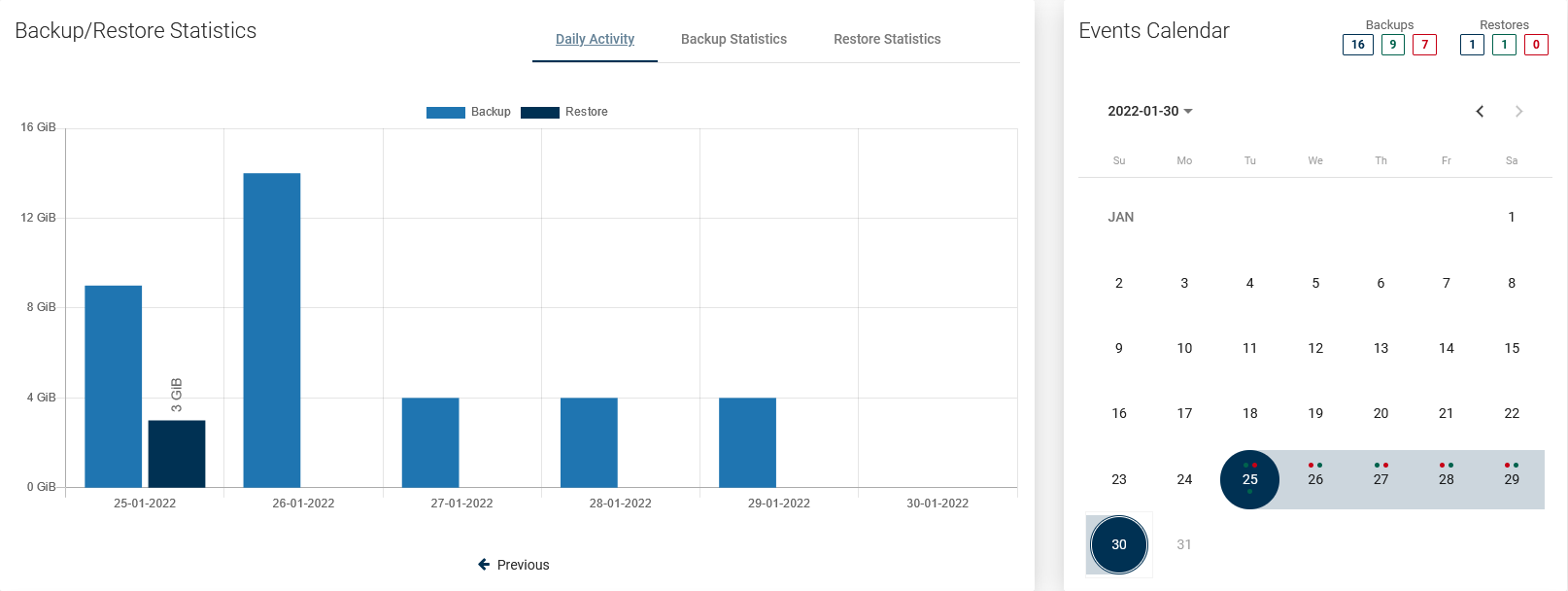
The calendar extends the possibilities of adjacent statistics. It allows you to neatly define the range of days you want to see, additionally makes a quick summary of the number of backups and restores (top right corner). Blue - the sum of all backups, Green - the sum of successes, Red - the sum of failures.
Bottom menu
In the bottom menu, you can find a large number of tabs, each of which will present different information or will allow you to change the configuration of this particular virtual machine.
Backup
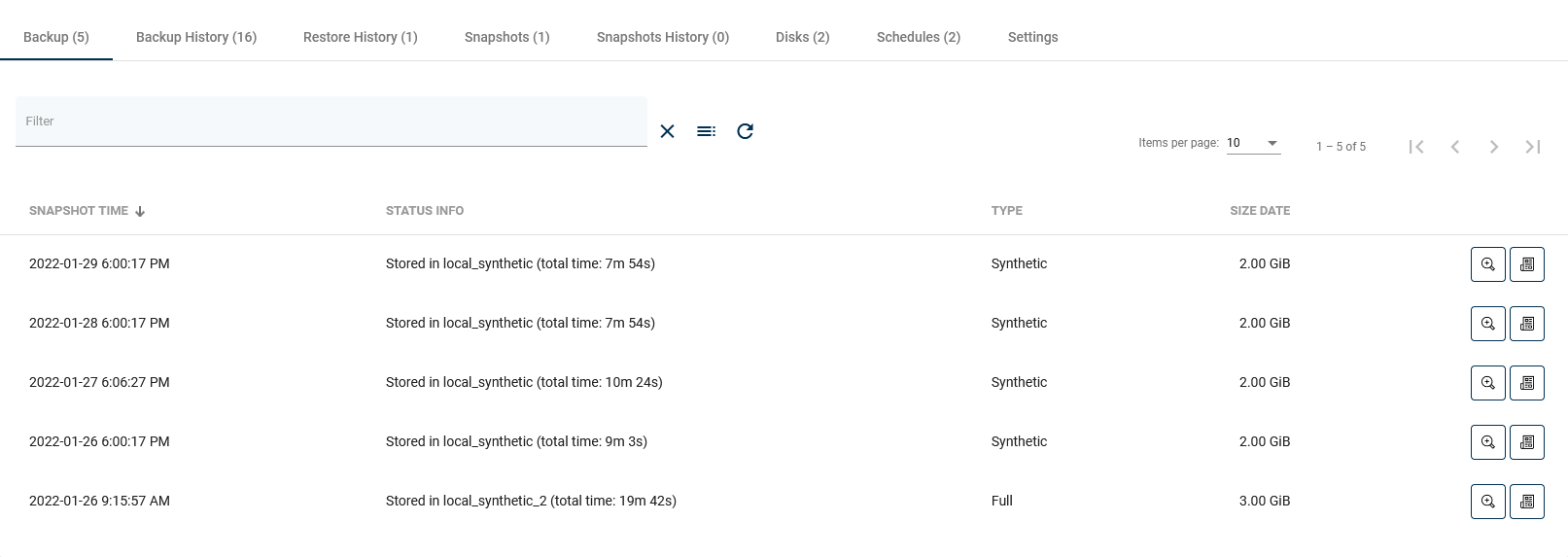
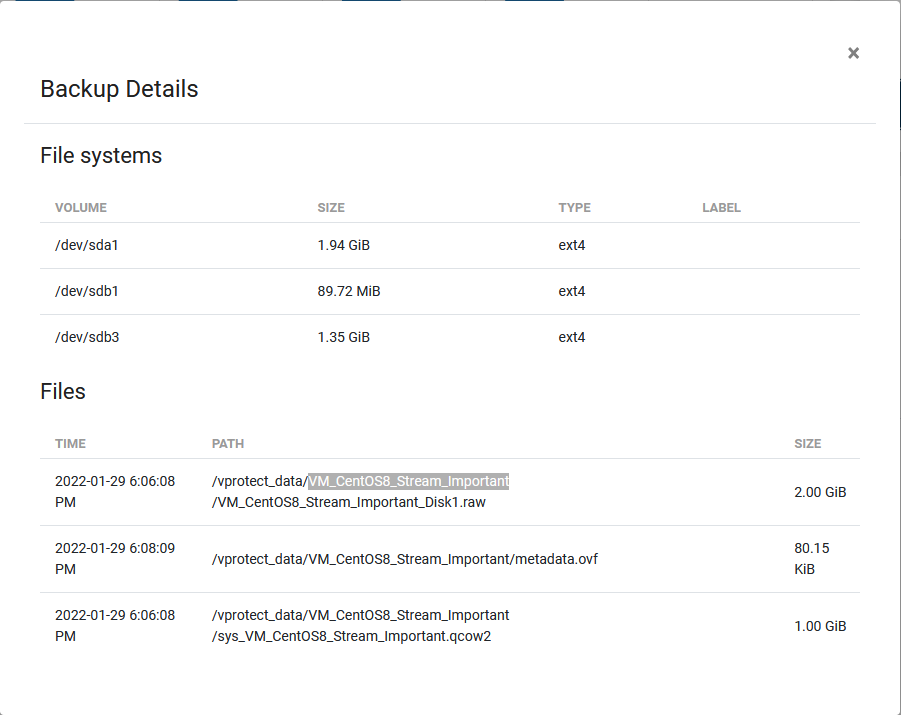
The first tab shows all virtual machine backups that are currently available and all basic information about them in a list. After clicking on the magnifying glass button, you will see additional information. The button next to it allows you to download logs in the form of a .txt file.
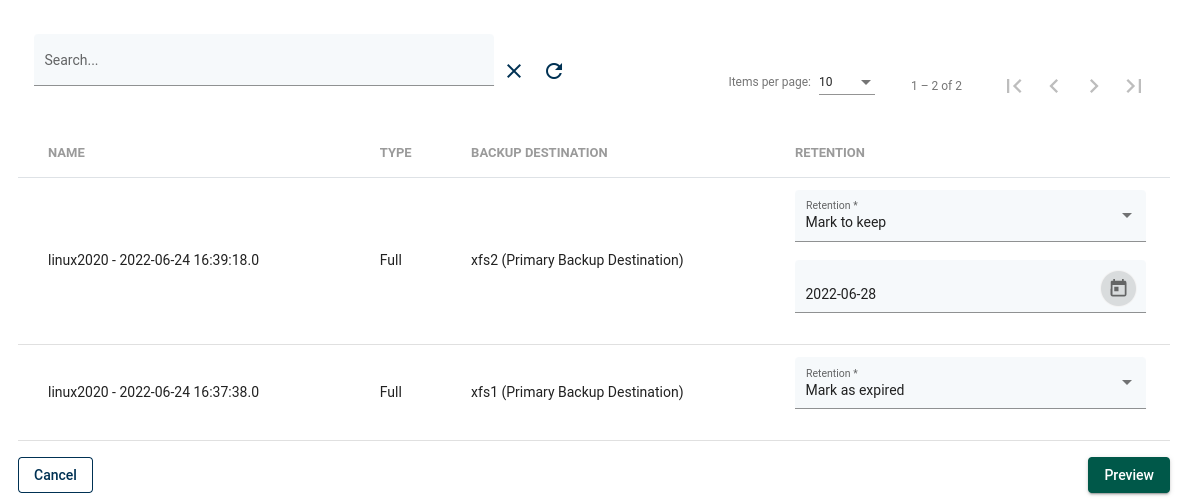
Adjust Retention
On the list of backups, you can also adjust retention for selected backups. Each backup can be set to:
"Mark to keep" which will keep the backup from being deleted by retention up to the set date
"Mark as expired" which will mark backup for removal during next backup cleanup process
Backup History
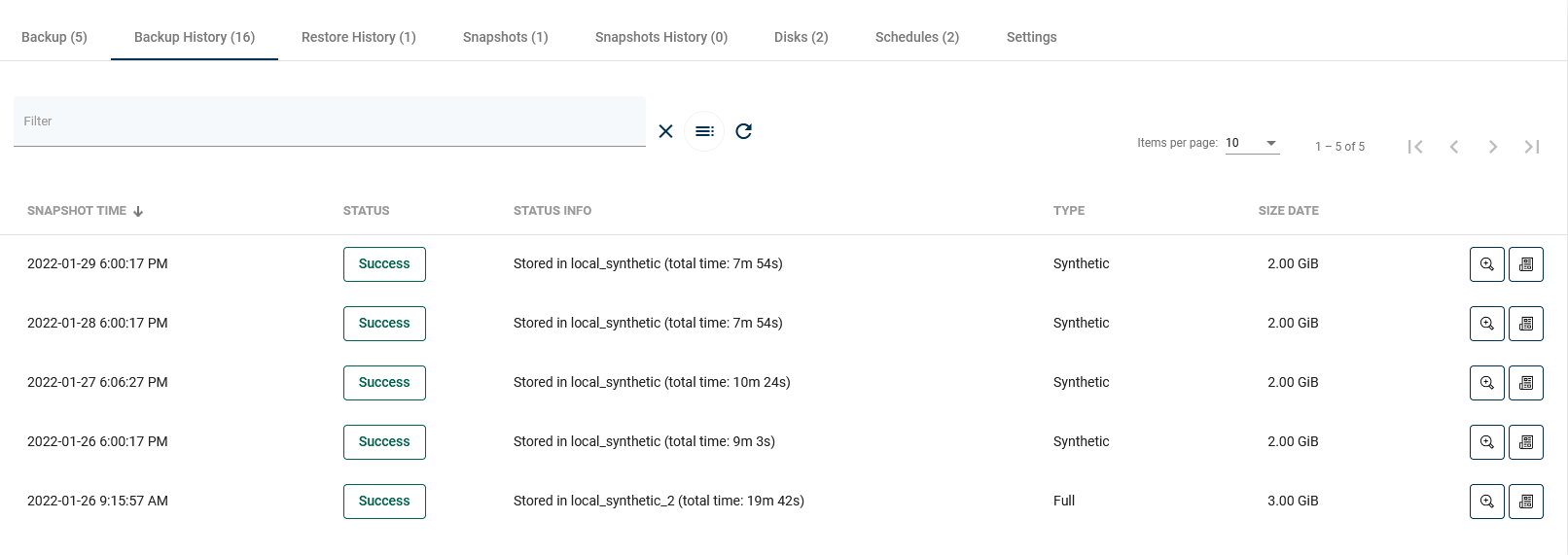
This tab shows information about all backups made for this virtual machine, as well as information about failed, removed (because of retention), or currently executing backups.
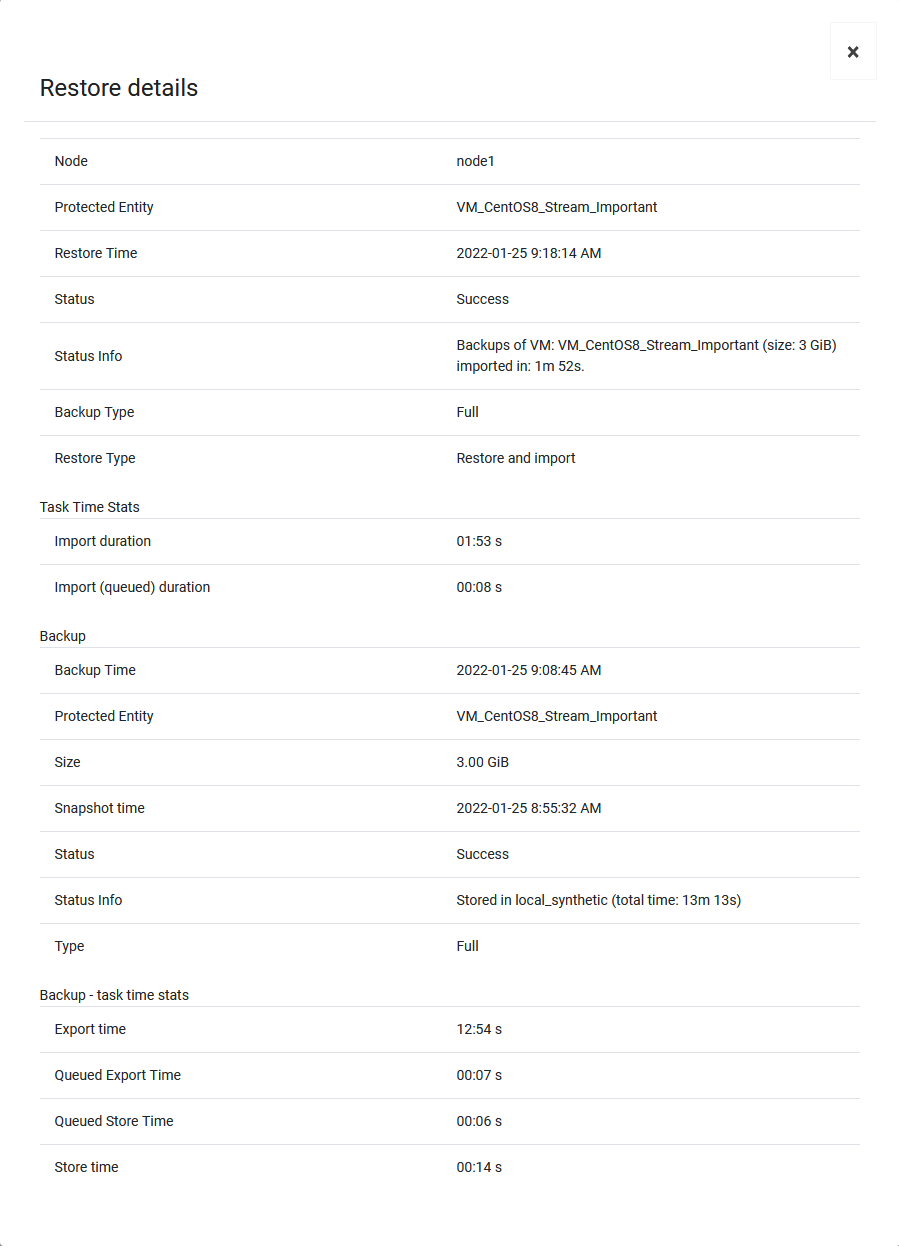
Restore History
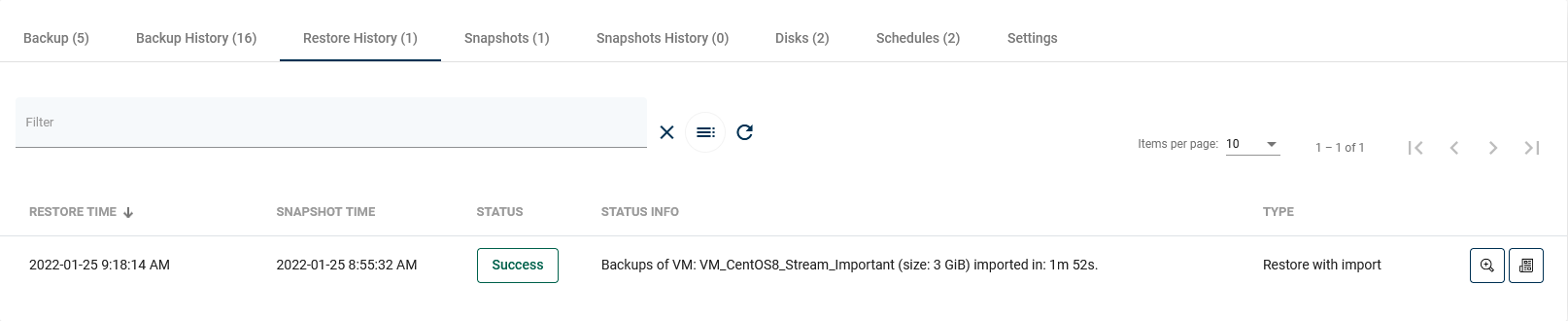
This tab is similar to "Backup History". This is a list with basic information about the virtual machine restores performed. When you open the details of the selected restore, you will see more detailed information.
Snapshots
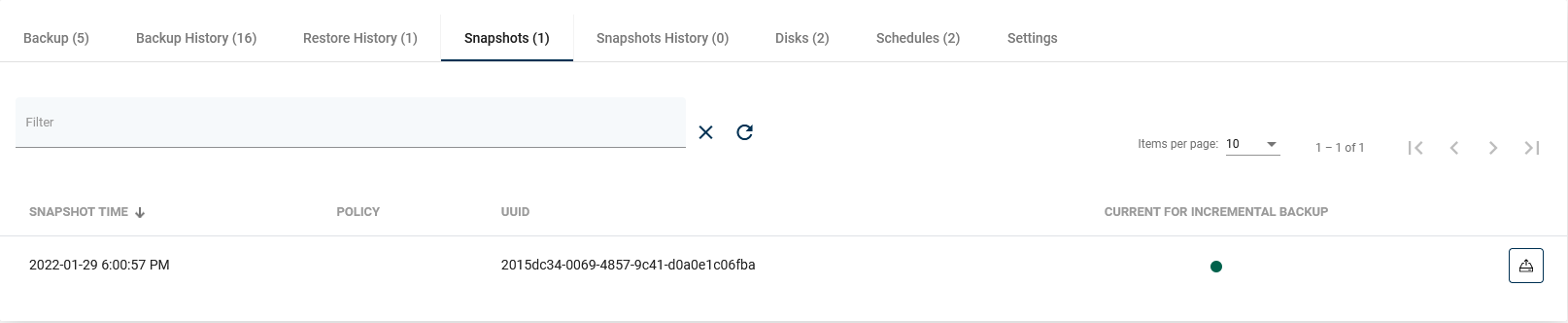
This tab shows virtual machine snapshots (remember - snapshots are stored on the hypervisor). The snapshot can be divided into two categories:
1. As you can see in the list above, there is a green dot next to the snapshot. This means that this snapshot is created for incremental backup purposes. This is an automatic operation and we only keep the last snapshot.
2. The second one on the list is a snapshot created at the user's request (scheduled or manual).
Next to the snapshot is a button that allows you to restore the virtual machine. It actually creates a new virtual machine and keeps the old one (security considerations to protect against the human factor).
Disks
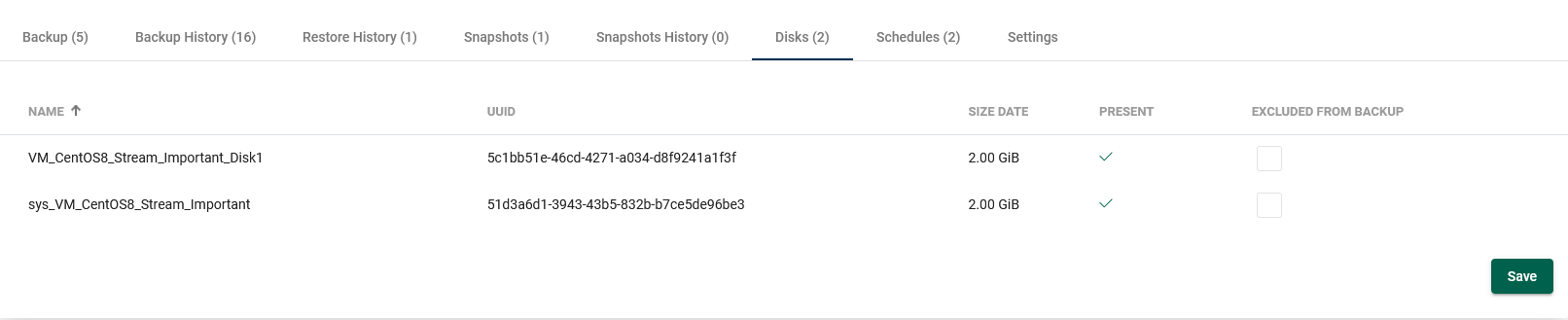
It is worth remembering that if such a virtual machine is restored, the excluded disks will be created from scratch and connected to the machine.
Schedules
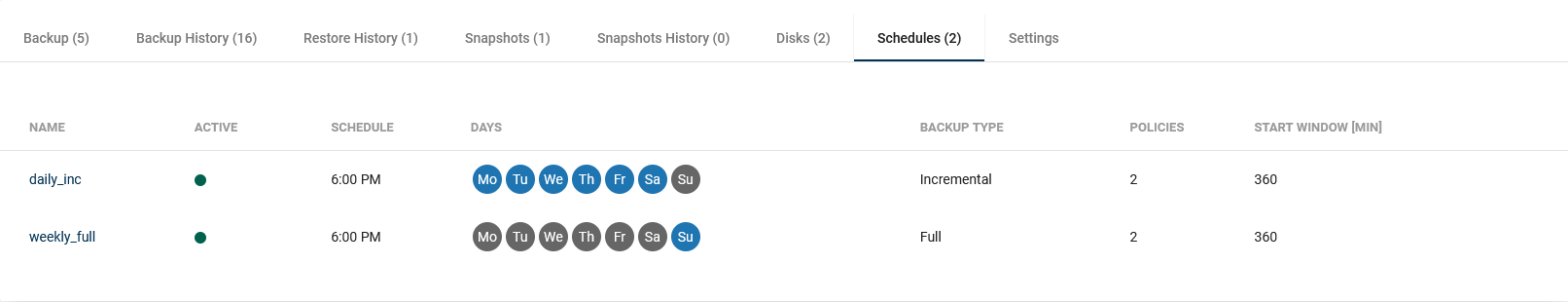
In this tab, you can see all the schedules assigned to the virtual machine.
Mounted Backups
This tab shows a list of mounted backups for this virtual environment.
Settings
Finally, the last tab. The first two options allow you to change the policies assigned to the virtual machine. The third is a toggle to turn on or off the "Snapshot consistent technology" feature. Below, You can change the transfer mode which is used for this VM.
Performing pre- / post-snapshot commands is a function intended for advanced users. As the name implies, it allows us to execute scripts via ssh or winrm connection, either before or after taking a snapshot.